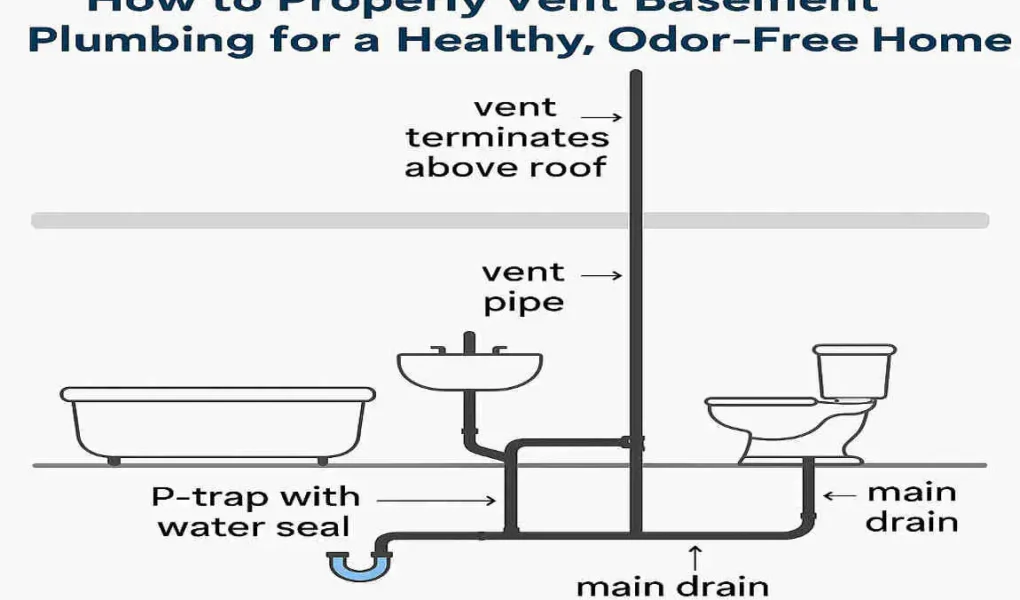
Are you tired of dealing with unpleasant odors and slow drainage in your basement? Proper basement plumbing ventilation is the key to maintaining a healthy home environment and preventing these issues.
Understanding Basement Plumbing Ventilation
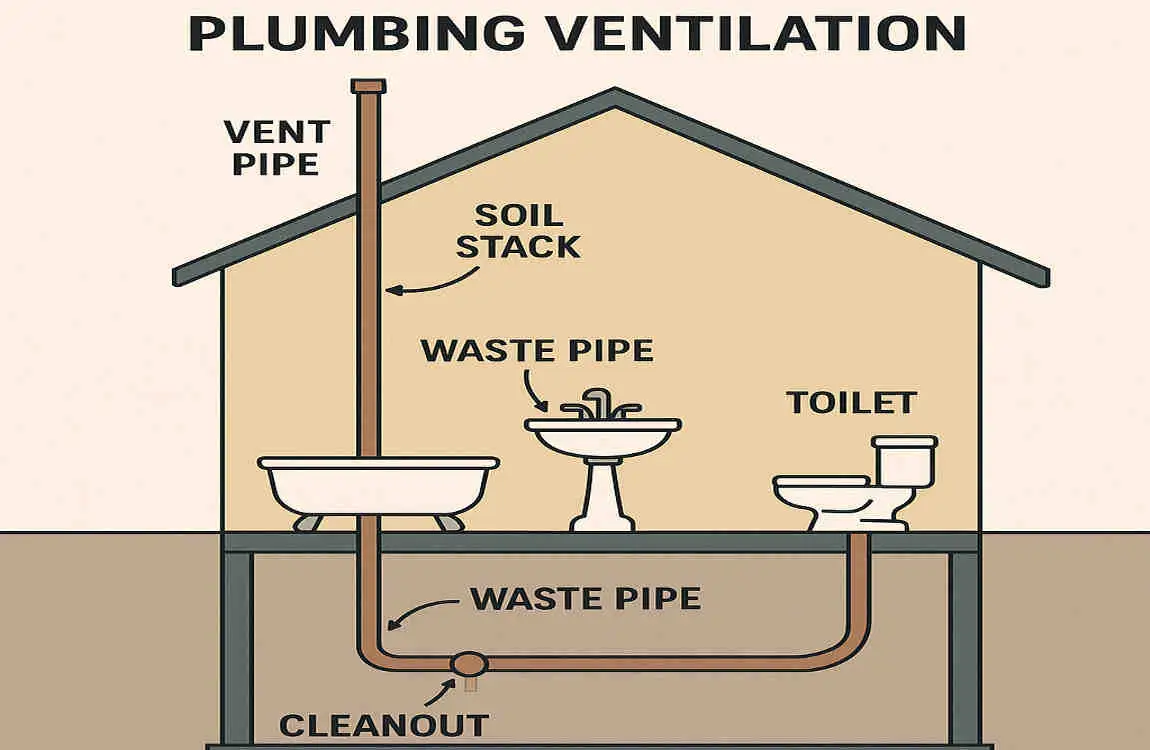
What is Basement Plumbing Ventilation?
Basement plumbing ventilation is the system of pipes and components that allow air to flow through your plumbing. This airflow is crucial for maintaining proper drainage and preventing the buildup of sewer gases.
The Role of Venting in Water Drainage and Sewer Gas Control
Proper venting helps balance pressure in your plumbing system, allowing water to flow freely through the pipes. When the pressure is balanced, water can drain quickly and efficiently, reducing the risk of slow drainage and clogs.
Additionally, venting plays a vital role in controlling sewer gases. These gases are byproducts of decomposition in your septic system or municipal sewer line. Without proper venting, these gases can escape into your basement, causing unpleasant odors and potential health hazards.
Common Problems Caused by Poor Basement Plumbing Venting
If your basement plumbing is not vented correctly, you may experience several issues, including:
- Unpleasant odors emanating from drains and fixtures
- Slow drainage or gurgling sounds in sinks, toilets, and showers
- Clogs and backups in your plumbing system
These problems can be frustrating and may lead to more severe issues if left unaddressed. That’s why it’s essential to ensure your basement plumbing is adequately vented.
The Basics of How to Vent Basement Plumbing
Components Involved in Basement Plumbing Venting
To properly vent your basement plumbing, you’ll need to understand the key components involved:
- Drain Pipes: These pipes carry wastewater from your fixtures to the main drainage stack.
- Vent Pipes: These pipes allow air to enter the plumbing system, balancing pressure and facilitating smooth drainage.
- Traps: These curved sections of pipe hold a small amount of water, creating a seal that prevents sewer gases from entering your home.
- Air Admittance Valves (AAVs): These devices allow air to enter the plumbing system while preventing sewer gases from escaping.
The Role of the Main Drainage Stack
The main drainage stack is the central pipe that carries wastewater from your home to the sewer or septic system. It plays a crucial role in venting your basement plumbing by providing a direct path for air to enter the system.
The Importance of P-Traps
P-traps are essential for preventing sewer gases from entering your home. These curved sections of pipe hold a small amount of water, forming a seal that prevents gases from escaping. Every fixture in your basement should have a properly installed P-Trap to ensure a healthy living environment.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Vent Basement Plumbing Correctly
Now that you understand the basics of basement plumbing venting, let’s dive into a step-by-step guide to venting your basement plumbing correctly.
Locating the Main Drainage Stack and Connection Points
The first step in venting your basement plumbing is to locate the main drainage stack and identify the connection points for your basement fixtures. The main drainage stack is typically located in a wall or chase and runs vertically from your basement to the roof.
Installing P-Traps for All Basement Fixtures
Once you’ve located the main drainage stack, it’s time to install P-Traps for all your basement fixtures. This includes toilets, sinks, showers, and any other fixtures that drain into the system.
To install a P-Trap, follow these steps:
- Measure the distance between the fixture drain and the main drainage stack.
- Cut a section of pipe to the appropriate length.
- Attach the P-Trap to the fixture drain and the main drainage stack, ensuring a secure, airtight connection.
Designing the Venting System
With your P-Traps in place, it’s time to design your venting system. This involves correctly sizing and positioning your vent pipes.
Vent Pipe Sizing
The minimum diameter for vent pipes is typically 1.5 inches. However, you may need to use larger pipes depending on the number of fixtures and the distance between the fixtures and the main drainage stack.
Proper Vent Pipe Positioning
Vent pipes should be positioned relative to the traps to ensure proper airflow. The vent pipe should be connected to the drain pipe on the upstream side of the trap, allowing air to enter the system and balance the pressure.
Using Air Admittance Valves (AAVs) as Alternatives
In some cases, you may not have the space or ability to install a traditional vertical vent stack. In these situations, you can use Air Admittance Valves (AAVs) as an alternative.
AAVs are devices that allow air to enter the plumbing system while preventing sewer gases from escaping. They can be installed directly on the drain pipe, eliminating the need for a vertical vent stack.
Ensuring Airtight, Secure Connections
Regardless of the venting configuration you choose, ensure all connections are airtight and secure. Leaks in the venting system can cause sewer gas to escape and other issues.
Use appropriate plumbing fittings and sealants to create secure connections between the vent pipes, drain pipes, and fixtures. Regularly inspect these connections to ensure they remain airtight.
Tools and Materials Needed for Proper Venting
To properly vent your basement plumbing, you’ll need a few essential tools and materials:
- Plumbing tools: Pipe cutter, pipe wrench, Teflon tape, and a hacksaw.
- Vent pipe materials: PVC or ABS pipes, fittings, and connectors.
- P-Traps: Pre-formed P-Traps or the materials to create custom P-Traps.
- Air Admittance Valves (AAVs): If using AAVs as an alternative to vertical vent stacks.
Safety Precautions During Installation
When working on your basement plumbing, it’s essential to take safety precautions to protect yourself and your home:
- Wear protective gear, including gloves and safety glasses.
- Turn off the water supply before beginning any plumbing work.
- Use caution when cutting pipes to avoid injury.
- Follow all manufacturer instructions for the tools and materials you’re using.
Common Venting Configurations for Basement Plumbing
There are several standard venting configurations you can use for your basement plumbing, depending on your specific needs and space constraints.
Traditional Vent Stack Connection
The traditional vent stack connection involves running a vertical vent pipe from the drain pipe to the roof. This configuration provides a direct path for air to enter the plumbing system and is often the most effective venting solution.
Use of AAVs in Tight or Retrofit Spaces
If you don’t have the space or ability to install a traditional vent stack, you can use Air Admittance Valves (AAVs) as an alternative. AAVs can be installed directly on the drain pipe, allowing air to enter the system while preventing sewer gases from escaping.
Venting Multiple Fixtures with Shared Vents
In some cases, you can vent multiple fixtures using a shared vent. This configuration involves connecting the vent pipes from various fixtures to a single vent stack, reducing the number of vent pipes needed.
However, it’s essential to ensure that the shared vent is appropriately sized and positioned to accommodate the airflow needs of all the connected fixtures.
How Proper Venting Prevents Odors and Maintains Healthy Air Quality
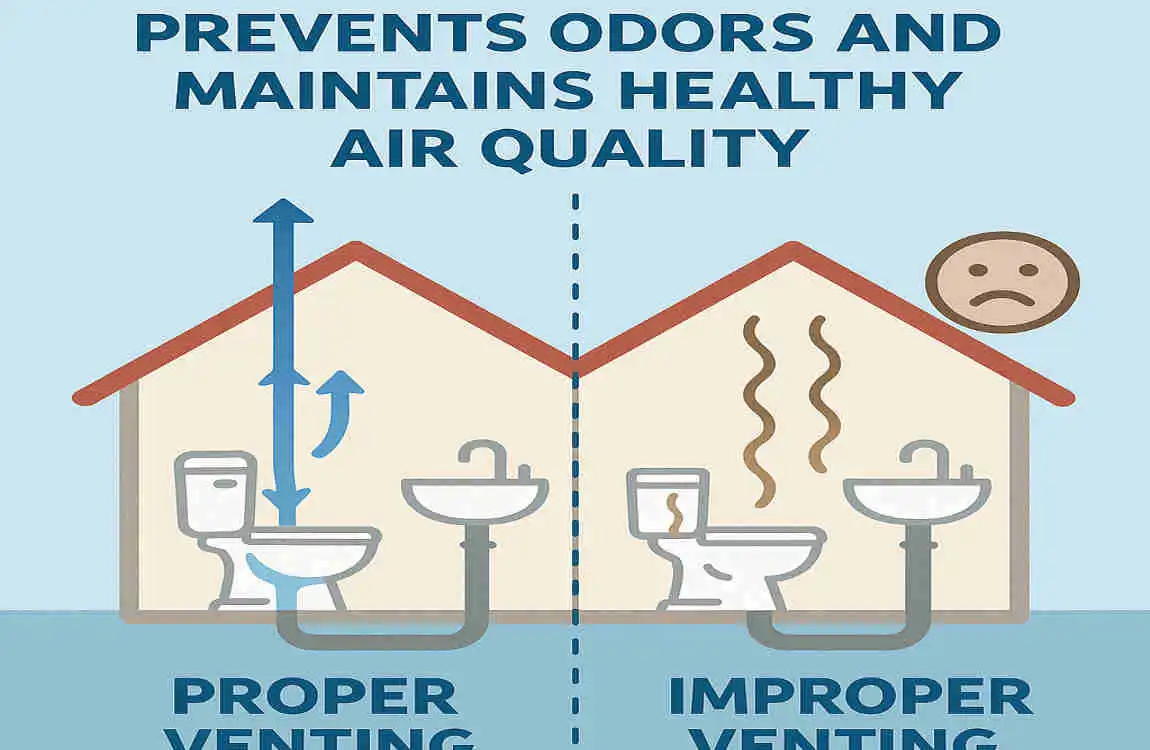
Proper venting plays a crucial role in preventing odors and maintaining healthy air quality in your basement.
Preventing Sewer Gas Escape
Sewer gases are a byproduct of the decomposition process in your septic system or municipal sewer line. These gases can be hazardous to your health and can cause unpleasant odors in your home.
Proper venting prevents sewer gas from escaping by allowing air to enter the plumbing system and balancing the pressure. This balanced pressure keeps the P-Traps filled with water, creating a seal that blocks the gases from entering your basement.
Balancing Pressure for Smooth Drainage
In addition to preventing sewer gas from escaping, proper venting also helps balance the pressure within your plumbing system. This balanced pressure allows water to flow freely through the pipes, reducing the risk of slow drainage and clogs.
When pressure is imbalanced, it can create a vacuum effect that slows drainage. By allowing air to enter the system, venting helps to maintain a consistent pressure and ensure smooth, efficient drainage.
Importance of Regular Inspection and Maintenance
To ensure your basement plumbing remains properly vented and odor-free, it’s essential to perform regular inspections and maintenance.
Check your vent pipes and connections periodically to ensure they remain airtight and secure. Clear any blockages or debris from the vent openings to allow air to flow freely through the system.
If you notice any signs of venting issues, such as odors or slow drainage, address them promptly to prevent more severe problems from developing.
Troubleshooting and Fixing Venting Problems in Basements
Even with proper venting, you may still encounter issues with your basement plumbing. Here are some common signs of venting problems and how to address them:
Identifying Signs of Venting Issues
- Gurgling sounds: If you hear gurgling sounds coming from your drains or fixtures, it may indicate a venting issue.
- Slow drainage: Slow drainage can be a sign of an imbalanced pressure in your plumbing system, which may be caused by improper venting.
- Odors: Unpleasant odors emanating from your drains or fixtures can indicate sewer gas escape due to venting problems.
Quick Fixes to Improve Venting
If you suspect a venting issue, there are a few quick fixes you can try before calling a professional:
- Check for blockages: Inspect your vent pipes and openings for any blockages or debris that may be restricting airflow.
- Tighten connections: Ensure all vent pipe connections are secure and airtight to prevent leaks and pressure imbalances.
- Install an AAV: If you’re unable to install a traditional vent stack, consider adding an Air Admittance Valve (AAV) to improve venting.
When to Call a Professional Plumber
If your quick fixes don’t resolve the issue or you’re unsure how to vent your basement plumbing properly, it’s best to call a professional plumber.
A licensed plumber can assess your plumbing system, identify any venting issues, and provide the necessary repairs or modifications to ensure proper venting and a healthy, odor-free home.
Best Practices and Tips for Maintaining a Proper Vent System
To keep your basement plumbing properly vented and maintain a healthy, odor-free home, follow these best practices and tips:
Regular Vent Pipe Inspections
Perform regular inspections of your vent pipes and connections to ensure they remain airtight and secure. Check for any signs of leaks, corrosion, or damage that may affect the venting system.
Keeping Vent Openings Clear of Blockages
Keep your vent openings free of blockages or debris that could restrict airflow. Regularly clean the vent openings and remove any leaves, dirt, or other materials that may accumulate over time.
Periodic Checks for Leaks or Loose Fittings
Periodically check your vent pipes and connections for any leaks or loose fittings. Tighten any loose connections and repair any leaks promptly to maintain proper venting and prevent sewer gas escape.