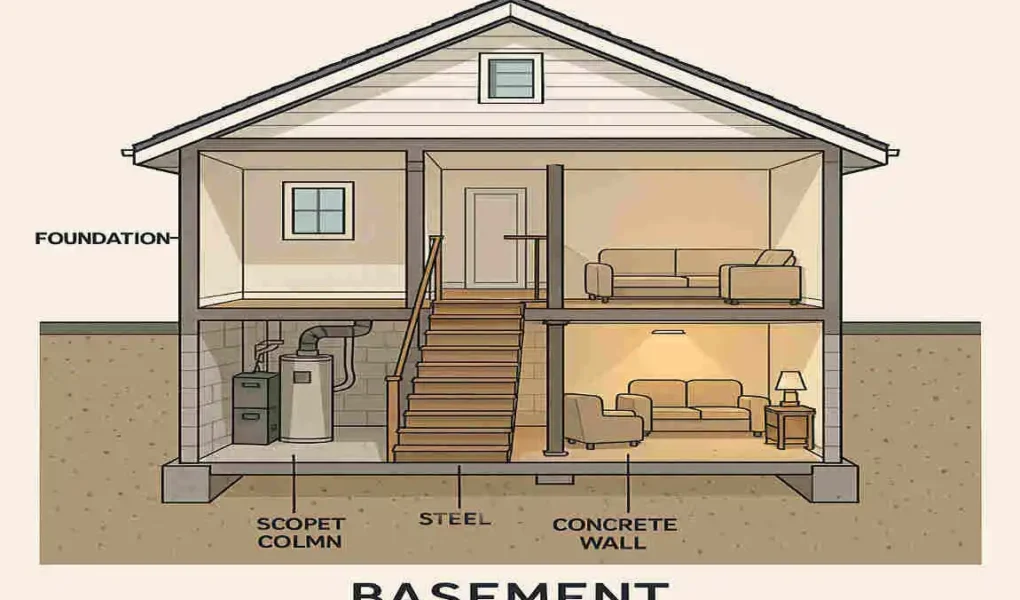
Have you ever wondered what that mysterious space beneath your home is all about? If you’re a homeowner or considering building a new house, understanding basements is crucial.
What Is a Basement in a Building?
Before we delve into the nitty-gritty, let’s first define what a build basement is in the context of residential buildings. Simply put, a cellar is an underground level of a house that is partially or entirely below ground level. It’s like having a secret room beneath your home, waiting to be discovered and put to use.
Types of Basements
Basements come in various shapes and sizes, each with its own unique characteristics. Here are some common types:
- Full Basement: This type of basement spans the entire footprint of the house above it, providing maximum space for storage or additional living areas.
- Partial Basement: As the name suggests, a partial basement only covers a portion of the house’s footprint, often due to site constraints or design choices.
- Walk-Out Basement: Also known as a daylight basement, this type features one or more walls exposed above ground level, providing easy access and natural light.
- Daylight Basement: Similar to a walk-out basement, a daylight basement features windows or doors that open to the outside, allowing for ample natural light.
Basements vs. Cellars vs. Crawl Spaces
It’s easy to get confused between basements, cellars, and crawl spaces, but they each serve different purposes:
- Basement: As we’ve discussed, a cellar is a habitable space beneath a house, often used for storage, living areas, or utilities.
- Cellar: A cellar is typically a smaller, less finished space used for storage, often with lower ceilings and limited access.
- Crawl Space: A crawl space is a narrow gap between the ground and the first floor of a house, used for access to plumbing, electrical, and HVAC systems.
Basements in the Overall Structure of a House
Basements play a crucial role in the overall structure of a house, serving as the foundation upon which the rest of the building rests. They help distribute the weight of the home evenly, providing stability and support.
Purpose of a Basement in a House
Now that we understand what a basement is, let’s examine its various purposes within a house.
Structural Support and Foundation Benefits
One of the primary purposes of a basement is to provide structural support for the house above it. The basement walls and floor help distribute the home’s weight evenly, preventing uneven settling and potential damage.
Space Utilization
Basements offer a wealth of additional space that can be used for various purposes. From storage and utility rooms to additional living areas, the possibilities are endless. Imagine having a home gym, a cozy family room, or even a rental unit right beneath your feet!
Protection Against Weather and Environmental Factors
Basements can serve as a protective barrier against harsh weather conditions and environmental factors. They can help insulate the house from extreme temperatures, reduce noise from outside, and even provide a safe haven during severe storms or tornadoes.
Impact on Property Value and Resale Potential
Having a basement can significantly impact the value and resale potential of a property. It adds usable square footage to the house, making it more attractive to potential buyers. Additionally, a well-designed and finished basement can make your home stand out from others on the market.
Benefits of Having a Basement
Now that we’ve covered the purposes of a basement, let’s explore the numerous benefits it offers.
Increased Usable Square Footage
One of the most apparent benefits of having a basement is the increased usable square footage it provides. Without expanding the footprint of your house, you can gain a whole new level of living space, perfect for growing families or those who love to entertain.
Versatility
Basements are incredibly versatile spaces that can be adapted to suit your needs. Here are just a few ideas:
- Home Office: Create a quiet and private workspace away from the hustle and bustle of the main living areas.
- Gym: Set up a home gym with all your favorite equipment, saving you time and money on gym memberships.
- Entertainment Room: Transform your basement into the ultimate entertainment zone with a home theater, game room, or bar area.
- Rental Unit: If local regulations allow, consider converting your basement into a rental unit to generate additional income.
Energy Efficiency and Insulation Advantages
Basements can contribute to the overall energy efficiency of your home. By providing an additional layer of insulation, they help regulate the temperature and reduce energy costs. Additionally, the earth surrounding the basement acts as a natural insulator, keeping the space cooler in the summer and warmer in the winter.
Safety Benefits
In areas prone to severe weather, such as tornadoes, basements can serve as a safe haven during emergencies. They provide a sturdy and protected space where you and your family can seek shelter until the danger has passed.
Building Essentials for Basements
Now that we’ve explored the purposes and benefits of basements, let’s dive into the essential elements of building one.
Site and Soil Considerations
Before you start digging, it’s crucial to consider the site and soil conditions. The type of soil, water table levels, and slope of the land can all impact the feasibility and cost of building a basement. Consulting with a geotechnical engineer can help you make informed decisions and prevent potential issues in the future.
Key Components
Building a basement requires careful attention to several key components:
- Foundation Walls: The foundation walls provide the structural support for the basement and the house above it. They are typically constructed using concrete or masonry materials.
- Flooring: The basement floor is usually made of concrete and should be properly sloped to allow for drainage.
- Waterproofing: Waterproofing is crucial in preventing moisture and water damage in the basement. This can include exterior membranes, drainage systems, and interior sealants.
Proper Drainage and Moisture Control
Ensuring proper drainage and moisture control is crucial for maintaining a dry and healthy basement. This can involve installing drainage systems, such as French drains or sump pumps, and implementing proper grading around the foundation to direct water away from the house.
Structural Requirements
Basements must meet specific structural requirements to ensure the safety and stability of the house. This includes load-bearing walls, reinforcements, and proper anchorage to the foundation.
Ventilation and Air Quality
Maintaining proper ventilation and air quality in the basement is essential for creating a comfortable and healthy living space. This can involve installing mechanical ventilation systems, dehumidifiers, and ensuring adequate air circulation.
Insulation Techniques
Insulating a basement can help regulate temperature, reduce energy costs, and prevent moisture issues. Standard insulation techniques include installing rigid foam boards, spray foam, or fiberglass batts on the walls and ceiling.
Common Basement Construction Methods
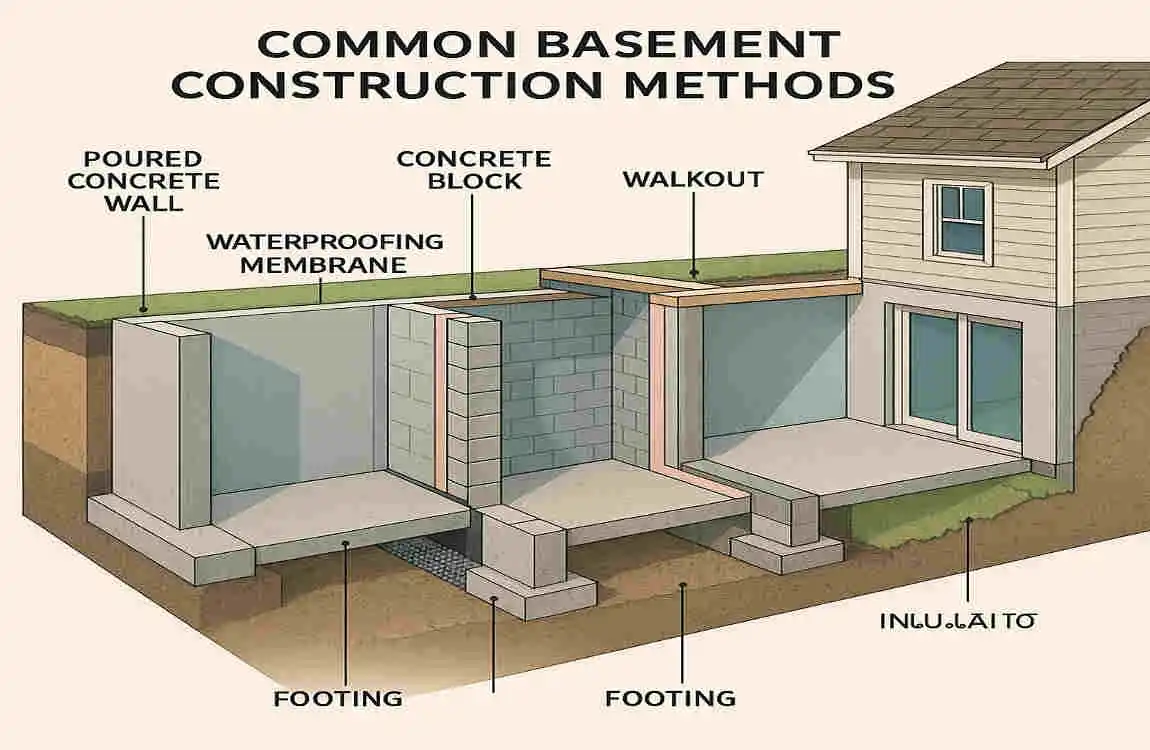
Now that we’ve covered the essential elements of building a basement, let’s explore some standard construction methods.
Excavation Processes and Foundation Types
The first step in building a basement is excavation, which involves removing soil to create space for the foundation. The type of foundation used can vary depending on factors such as soil conditions, local building codes, and design preferences. Common foundation types include poured concrete, concrete block, and precast concrete.
Materials Used
Building a basement requires the use of various materials, including:
- Concrete: Used for foundation walls, floors, and structural elements.
- Masonry: Brick, stone, or concrete blocks can be used for foundation walls and decorative elements.
- Waterproof Membranes: Applied to the exterior of the foundation walls to prevent water infiltration.
Typical Construction Timeline and Key Stages
The construction of a basement typically follows a series of key stages:
- Site Preparation: Clearing the site, excavating, and preparing the soil for foundation work.
- Foundation Construction: Pouring the foundation walls and floor, installing waterproofing and drainage systems.
- Framing and Rough-In: Framing the walls, installing plumbing, electrical, and HVAC systems.
- Insulation and Finishing: Installing insulation, drywall, and finishing touches such as flooring and trim.
Challenges and Solutions
Building a basement can present various challenges, such as:
- Water Management: Ensuring proper drainage and waterproofing to prevent moisture issues.
- Soil Conditions: Dealing with unstable or expansive soils that can impact the foundation.
- Cost and Budgeting: Managing the costs associated with excavation, materials, and labor.
By working with experienced professionals and carefully planning each stage of the construction process, these challenges can be overcome, resulting in a successful and functional basement.
Waterproofing and Moisture Management
One of the most critical aspects of building a basement is ensuring proper waterproofing and moisture management. Let’s explore why this is so important and how to achieve it.
Why Waterproofing Is Critical
Waterproofing is crucial for preventing water damage, mold growth, and structural issues in basements. Without proper waterproofing, water can seep through the foundation walls and floor, resulting in a range of problems.
Waterproofing Methods and Materials
There are several methods and materials used for waterproofing basements:
- Exterior Waterproofing: Applying a waterproof membrane to the exterior of the foundation walls, combined with proper drainage systems.
- Interior Waterproofing: Using sealants, coatings, and drainage systems on the interior of the basement to manage water and moisture.
- Drainage Systems: Installing French drains, sump pumps, and other drainage solutions to direct water away from the foundation.
Signs of Basement Water Issues
It’s essential to be aware of the signs of basement water issues, such as:
- Water stains or discoloration on walls and floors
- Musty odors or visible mold growth
- Cracks in the foundation walls or floor
- Pooling water or dampness in the basement
If you notice any of these signs, it’s crucial to address the issue promptly to prevent further damage.
Maintenance Tips
To keep your basement dry and mold-free, follow these maintenance tips:
- Regularly inspect the exterior of the foundation for cracks or damage
- Ensure proper grading around the foundation to direct water away from the house
- Clean and maintain gutters and downspouts to prevent water buildup near the foundation
- Use a dehumidifier to control moisture levels in the basement
- Address any water issues promptly to avoid further damage
By following these tips and implementing proper waterproofing measures, you can enjoy a dry and comfortable basement for years to come.
Basement Finishing and Design Ideas
Now that we’ve covered the essential elements of building a basement, let’s explore some popular ways to finish and personalize these spaces.
Finishing and Personalizing Basement Spaces
Finishing a basement can transform it from a utilitarian space into a comfortable and inviting living area. Here are some ideas to consider:
- Adding drywall and trim to create a finished look
- Installing flooring, such as carpet, tile, or engineered wood
- Painting the walls and ceiling to brighten up the space
- Adding built-in shelving or cabinets for storage and organization
- Incorporating a fireplace or wet bar for added comfort and convenience
Lighting Solutions
Basements often lack natural light, so it’s essential to incorporate effective lighting solutions. Consider the following options:
- Recessed lighting for general illumination
- Task lighting for specific areas, such as a home office or workshop
- Accent lighting to highlight architectural features or artwork
- Natural light alternatives, such as light tubes or solar tubes
Flooring Options
Choosing the right flooring for your basement can be a challenge, as it needs to withstand moisture and potential water issues. Here are some popular options:
Flooring Type: Pros and Cons
Carpet Comfortable, warm, and quiet Susceptible to moisture and mold
Tile: Durable, water-resistant, and easy to clean. It can be cold and hard underfoot
Engineered Wood Warm, attractive, and relatively durable. More expensive than other options
Vinyl Waterproof, affordable, and easy to install. Less durable than other options
Safety Considerations
When renovating a basement, it’s crucial to prioritize safety. Here are some key considerations:
- Egress windows: Ensure that the basement has at least one egress window that meets local building codes for size and accessibility.
- Smoke and carbon monoxide detectors: Install these essential safety devices throughout the basement.
- Proper electrical wiring and outlets: Ensure that all electrical work is done by a licensed professional and meets local building codes.
- Stairway and handrail safety: Make sure that any stairs leading to the basement have proper handrails and meet safety standards.
By keeping these safety considerations in mind, you can create a basement that is not only functional and attractive but also safe for you and your family.
Cost Considerations for Building a Basement
Building a basement can be a significant investment, so it’s essential to understand the cost considerations involved. Let’s examine the factors that can influence the cost of building a basement and offer some tips for managing your budget.
Factors Influencing Cost
Several factors can influence the cost of building a basement:
- Size: The larger the basement, the more it will cost to excavate, construct, and finish.
- Materials: The choice of materials, such as concrete, masonry, and waterproofing systems, can significantly impact the overall cost.
- Location: The cost of labor and materials can vary depending on your location, with urban areas typically being more expensive than rural areas.
- Design: The complexity of the design, including the number of rooms, plumbing, and electrical work, can also impact the cost.
Budgeting Tips and Cost-Saving Strategies
To manage your budget and save on costs, consider the following tips:
- Get multiple quotes: Obtain quotes from several contractors to ensure you’re getting the best price for the work.
- Prioritize your needs: Focus on the most essential elements of your basement and consider phasing in less critical features over time.
- Consider DIY options: If you have the skills and time, consider tackling some aspects of the project yourself, such as painting or installing flooring.
- Shop around for materials: Compare prices from different suppliers to find the best deals on materials.
Comparing Cost vs. Value
When considering the cost of building a basement, it’s essential to weigh it against the potential value it can add to your home. A well-designed and finished basement can significantly increase your property’s value and appeal to potential buyers. Additionally, the added living space can provide long-term benefits for your family, making the investment worthwhile.
Legal and Code Requirements
Before you start building your basement, it’s crucial to understand the legal and code requirements that apply to your project. Let’s explore some key considerations.
Building Codes
Building codes are regulations that govern the construction of buildings to ensure safety and quality. When building a basement, you’ll need to comply with local building codes related to:
- Foundation design and construction
- Structural requirements
- Waterproofing and moisture management
- Egress windows and emergency exits
- Electrical, plumbing, and HVAC systems
Permits and Inspections
To ensure compliance with building codes, you’ll need to obtain the necessary permits and undergo inspections throughout the construction process. This typically involves:
- Applying for a building permit before starting work
- Scheduling inspections at key stages of the project, such as foundation, framing, and final completion
- Addressing any issues or violations identified during inspections
Safety Regulations
In addition to building codes, there are specific safety regulations that apply to basements, including:
- Egress windows: Basements used as living spaces must have at least one egress window that meets size and accessibility requirements.
- Ceiling height: The minimum ceiling height in a finished basement is typically 7 feet, although this can vary depending on local regulations.
- Exits: Basements must have a safe and accessible exit, such as stairs or a door leading to the outside.
By understanding and complying with these legal and code requirements, you can ensure that your basement is safe, functional, and meets the standards.
Common Misconceptions About Basements
There are several common misconceptions about basements that can lead to confusion and misinformed decisions. Let’s debunk some of these myths and clarify the facts.
Dampness and Mold
One common misconception is that all basements are damp and prone to mold growth. While it’s true that basements can be more susceptible to moisture issues, proper waterproofing and moisture management can prevent these problems. With the right approach, a basement can be just as dry and comfortable as any other part of the house.
Cost and Affordability
Another misconception is that building a basement is always expensive and unaffordable. While it’s true that constructing a basement can be a significant investment, the cost can vary depending on factors such as size, materials, and location. By carefully planning and budgeting, it’s possible to build a basement that fits within your financial means.
Usability and Functionality
Some people believe that basements are only suitable for storage and can’t be used as functional living spaces. However, with proper design and finishing, a basement can be transformed into a comfortable and versatile area for a variety of purposes, from home offices and gyms to entertainment rooms and rental units.
Basements vs. Cellars
There’s often confusion between basements and cellars, with some people using the terms interchangeably. However, as we discussed earlier, basements and cellars serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics. A basement is a habitable space that can be used for living areas, while a cellar is typically a smaller, less finished space used for storage.
Property Stability
Some people worry that building a basement can compromise the stability of their property. However, when constructed properly and in accordance with building codes, a cellar can actually enhance the stability of a house by providing a solid foundation and distributing weight evenly.
By understanding and addressing these common misconceptions, you can make informed decisions about building and utilizing a basement in your home.